The human body, as incredible as it is, is not invulnerable. Like most things in life, our bodies have limitations to what they can endure and require care to survive as we age. Our bodies are particularly susceptible to wear and tear, opening the door for serious diseases that make everyday function nearly impossible.
One of the most common issues arising from the constant wear we inflict on our bodies is arthritis. Arthritis is an extremely common issue among the American population and the human species. It is also one of the most debilitating physical maladies since it causes chronic pain and reduces our body’s range of motion.
While some treatment avenues for arthritis are well-known, other options might have escaped notice. One option that you might not have heard of is electrical stimulation. While electrical stimulation is not exactly a rare choice for physicians looking to treat arthritic symptoms, it is not commonly associated with the disease. While you might not be personally familiar with electrical stimulation, it is a very common and effective physical therapy treatment offered by chiropractic clinics and other physical therapy providers. The question of the hour is whether electrical stimulation can be used to treat arthritis.
What is Electrical Stimulation?
The first step to understanding how the treatment is of benefit is knowing what the treatment entails. As previously mentioned, electrical stimulation (e-stim) therapy is a form of physical therapy designed to alleviate physical pain and treat the conditions causing it. The process of electrical stimulation involves sending an electrical current through the body to alleviate pressure and relax the body. Electrical stimulation treatments help promote blood flow and strengthen muscles, allowing the body to block pain signals caused by problem areas of your anatomy.
Electrical stimulation therapy is a relatively straightforward treatment involving the application of small adhesive pads placed around the problem area. These pads are all connected to wires originating from the electrical stimulation device. Once the pads are placed, the device is activated, and the electrical current is transmitted from the device into your body. The sensation is not painful, and the voltage will only be increased until you feel a sensation similar to pins and needles in the padded area. There might be a few muscle twitches, but they are minor and not a sign of complication with the treatment.

The process itself generally lasts anywhere from 5 to 15 minutes total, with the duration varying with the underlying cause of the injury. But the short timeframe also means there is no downtime from the procedure, and you can go about your day without consequence. The only real preparation involved with electrical stimulation therapy happens before the pads are applied.
Your therapist will talk to you about allergies, current medication prescriptions, and any implanted devices you need to address before your session. Implanted devices like pacemakers cannot be removed and might preclude you from therapy, but you can suspend medication use before your first session.
Can Electrical Stimulation Help With Arthritis?
Arthritis, by nature, is a complex disease that can take many forms and almost always occurs in people who engage in repetitive motions daily. These motions slowly wear away at the padding, protecting joints from damage and causing inflammation. When this occurs, you will face chronic pain and discomfort that can lead to further complications if you do not seek treatment. While arthritis is a serious condition and lacks a cure, professionals can treat it, so the condition is manageable and does not make your day-to-day life a struggle.
Electrical stimulation therapy has many subtypes that have been tested to determine its efficacy in treating the symptoms of arthritis. Each variant of electrical stimulation therapy has slight differences, but one of the most commonly used versions is transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS). TENS follows the same general concept outlined in the previous section, using the adhesive pads connected to the electrical stimulation device. Through those pads, the current overrides the body’s pain signals to neutralize the pain felt due to the arthritic symptoms.
While the theory that TENS can treat the symptoms of arthritis is nice to believe, hard evidence is preferable. Fortunately, hard evidence is not difficult to find, given there have been studies assessing TENS’ ability to treat arthritis. TENS has been scientifically proven to treat acute and chronic pain alike, including the pain induced by osteoarthritis, the most common arthritic disease. Specifically, a 2015 Cochrane Review assessed the effects of TENS on patients with osteoarthritis. The review found that over half of the patients subjected to TENS therapy experienced a 50% reduction in their overall pain levels.

TENS is not the only form of electrical stimulation therapy tested as a treatment for arthritis. Another common avenue is electrical muscle stimulation (EMS), which uses similar technology to TENS to accomplish similar pain management results. EMS’ main function is as a rehabilitative treatment to help the patient recover from injuries. However, with relative success, EMS has been assessed as a pain management tool for arthritic conditions. A review of 7 different studies showed that 6 of the studies had favorable results for EMS as an arthritic pain management tool.
Unfortunately, the quality of those studies was somewhat lackluster. But the promising results of those studies maintain EMS as a viable pain management tool for those suffering from osteoarthritis or rheumatoid arthritis. Electrical stimulation therapy has multiple subtypes beyond TENS and EMS, but in all likelihood, your physical therapist will administer either of those 2 in particular. While electrical stimulation therapy does have encouraging results, it is also important to remember that every treatment is bound to have a downside.
What Are the Risks of Electrical Stimulation Therapy?
Virtually every treatment or medication available in modern treatments has some side effects or risks that make them imperfect. While most side effects are negligible and can be overcome with time, others are more dangerous. When it comes to electrical stimulation therapy, there is not much in the way of risk. Unfortunately, since electricity is involved, potential hazards depend on your situation.
We mentioned before that patients with implanted devices like pacemakers are precluded from using electrical stimulation therapy. This exclusion is due to the devices risking an overload when exposed to an electrical current. Having a current at any voltage run through your body could either short out the pacemaker or cause it to be destroyed.
If an implanted device is destroyed, it risks causing internal damage to your body. Pacemakers are connected to the cardiovascular system, so an overcharge could lead to heart trauma. Fortunately, the most severe risks associated with electrical stimulation therapy are associated with integrated devices. If you do not have technological implants, you do not have to worry about that risk. Unfortunately, this does not fully cover all the potential issues that might arise while using electrical stimulation therapy.
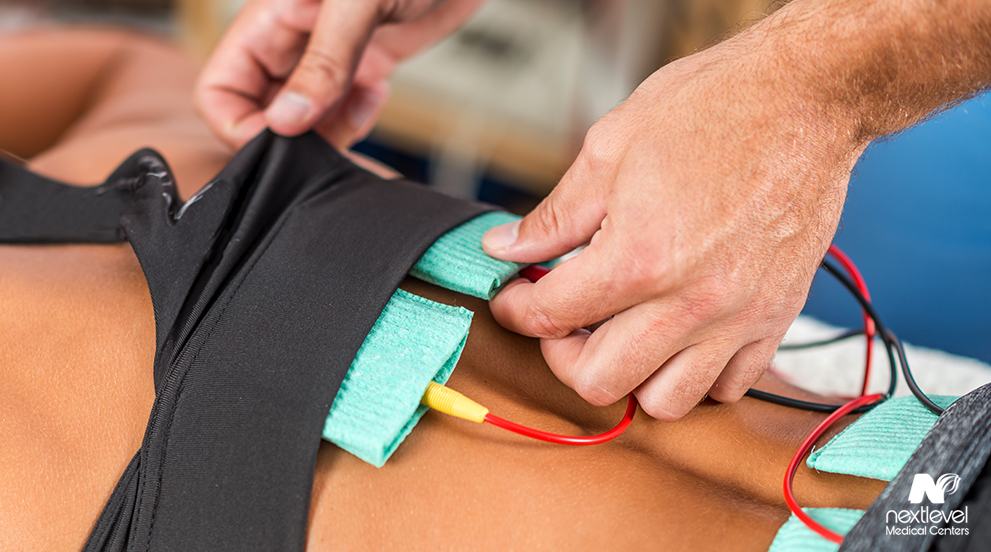

Another issue arises if the therapist overestimates the necessary voltage for the current. An electrical stimulation device does not pack enough of a punch to electrocute you to death. Still, an impulse that exceeds the necessary levels can adversely affect your physical health. Sometimes, the area beneath the electrode gets irritated and slightly damaged when exposed to the current. The adhesive itself can also cause mild irritation in some cases. Skin irritation is not a serious side effect of electrical stimulation therapy. Still, it is worth keeping in mind if you notice a rash or inflammation that was not present before your session.
Unfortunately, the voltage issue does not end with skin irritation. Excessive voltage can cause the patient to suffer a tissue burn at the electrode site. Tissue burns from electrical stimulation therapy are extremely rare since the therapist is trained to prevent such issues. Nevertheless, it is a potential problem if an inept therapist increases the current’s voltage beyond what is strictly necessary. If a tissue burn does occur, your therapist must immediately stop the treatment and apply the appropriate skin care to minimize the burn’s consequences.
While a tissue burn might seem like the most severe risk associated with electrical stimulation therapy, there is still one more concern. In a worst-case scenario, an excessive impulse can cause damage to the muscles beneath the skin. Electrical stimulation therapy is designed to cause the muscles to tense up somewhat, allowing the healing process to begin. If the current is too high, those muscle contractions become too severe and cause tearing. You can tell if the risk for muscle tearing increases if you feel intense muscle pain during the treatment. If this happens, your therapist must immediately stop the therapy and apply acute muscle injury treatment instead.
It is important to remember that these risks are extremely rare. Most therapists are trained to recognize your limits and avoid setting the current too high. If they do occur, it is likely a result of a poorly trained therapist. Fortunately, they are few and far between, and you should not have much cause to worry. If you have reservations about electrical stimulation therapy, there are alternatives available.
Alternatives to Electrical Stimulation Therapy
Although electrical stimulation therapy is generally a safe choice for your recovery, there are other options if the risks concern you. Arthritic conditions are usually treated by doctors, who employ medication and sometimes surgery to counter the effects. Physical therapists attempt to rework your body to heal what they can so you do not need more invasive treatments. Most physical therapists will focus on anti-inflammatory treatments to reduce the irritation in the joints and give your body time to recover. They usually default to their other main treatments when electrical stimulation therapy is not an option.
One of the best alternatives to electrical stimulation therapy is vibration therapy, which generally only has risks if you are on prescription medication. Vibration therapy involves using a device or platform to send vibrations through your body and trigger your body’s natural recovery responses.
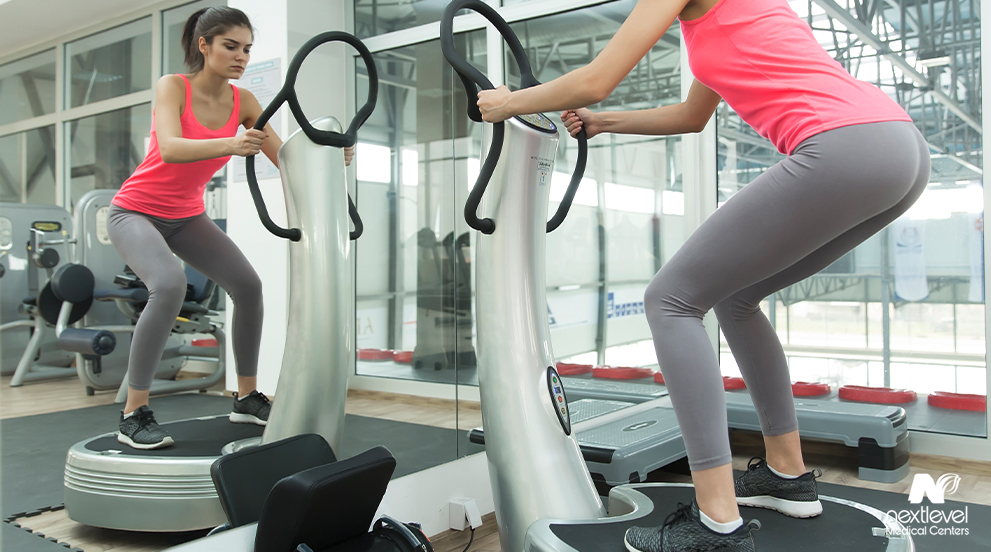

This can include:
- Improved blood circulation.
- Increased bone density.
- Increased muscle mass.
- Reduced physical stress.
Vibration therapy can offer serious benefits to recovering from arthritic conditions by triggering these responses. Vibration therapy also helps with weight loss, which helps keep the pressure off your joints, so your body weight does not exacerbate arthritic symptoms. Vibration and electrical stimulation therapy are only 2 of the treatments offered by physical therapists. But it does not matter how safe a particular treatment is if the one administering it is inept. Finding a reliable physical therapy clinic is the most important part of any treatment.
Take Your Health to the Next Level!
Electrical stimulation therapy is an increasingly common physical therapy treatment offered by clinics across the country. While having electrodes taped to your body might seem daunting, the procedure is extremely safe. The few risks it does carry are so rare that you will likely never experience them. The use of electrical stimulation therapy as a treatment for arthritis might seem even more ludicrous, but the efficacy of the treatment has a scientific foundation that makes it reliable.
Choosing to undergo electrical stimulation therapy might not be an overly difficult decision to make, especially if your pain is escalating. The real challenge is finding a provider who knows what they are doing and can offer the treatment for your needs.
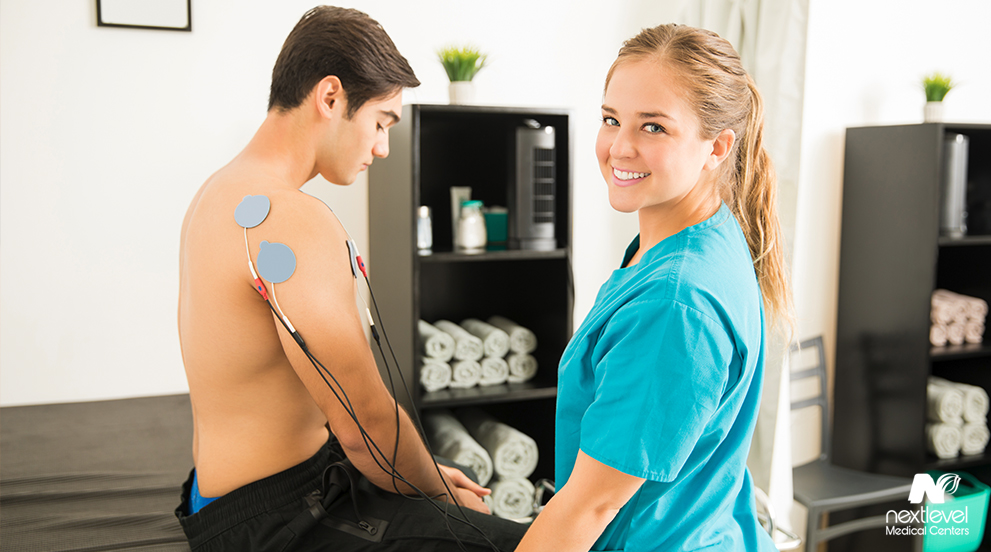
To that end, we at Ortho Integrative invite you to our facility. We offer a wide range of physical health treatments, from simple massage therapy to electrical stimulation therapy. Additionally, we staff licensed physicians more than qualified to offer safe and reliable treatment, so the rare risks associated with electrical stimulation therapy are nonexistent.
Arthritis is extremely painful, and living with it can be almost impossible, depending on the severity. So, we urge you to visit our website and assess the treatments for yourself. If you decide you want to try electrical stimulation therapy or any other treatment for your arthritis, feel free to stop by so we can take your health to the Next Level!
Have any questions or concerns about electrical stimulation therapy? If so, please do not hesitate to reach out and contact us! We would be be more than happy to answer any of your questions or clear up any potential concerns you may be having!




